Resources attached to the Road To DevOps tutorial
https://blog.noobtoroot.xyz/road-to-devops/
You can not select more than 25 topics
Topics must start with a letter or number, can include dashes ('-') and can be up to 35 characters long.
5.5 KiB
5.5 KiB
TP Ansible
Les bases
-
Préparer les machines cibles.
-
Créer un fichier d'inventory.
-
Vérifier le bon fonctionnement d'Ansible.
Vérifier la version de Ansible
ansible@ansible-0:~$ ansible --version
ansible 2.6.4
config file = /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
configured module search path = [u'/home/ansible/.ansible/plugins/modules', u'/usr/share/ansible/plugins/modules']
ansible python module location = /usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/ansible
executable location = /usr/bin/ansible
python version = 2.7.13 (default, Nov 24 2017, 17:33:09) [GCC 6.3.0 20170516]
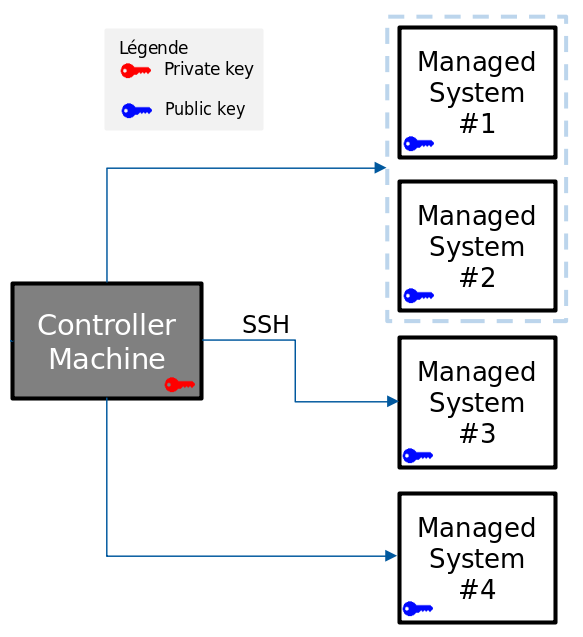
Préparer les machines cibles
Pour que Ansible puisse se connecter à des machines distantes, il faut :
-
Mettre en place une authentification
via une paire de clés ssh, -
Générer un fichier d'inventaire qui contiendra
la liste des machines.
Authentification via clés ssh
- Créer une paire de clés ssh
$ cd
$ ssh-keygen
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/home/ansible/.ssh/id_rsa):
Created directory '/home/ansible/.ssh'.
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in /home/ansible/.ssh/id_rsa.
Your public key has been saved in /home/ansible/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
The key fingerprint is:
SHA256:pipIK6HsauJKf2TuyRRWf/EYgUggRknBmtbIuGVq0/g ansible@ansible-0
The key's randomart image is:
+---[RSA 2048]----+
| +*o.o.. .. |
| .o. . . . |
|o = . o |
|.*o. . . = |
|.=o o S. o . |
|+= ..o.o . |
|=++ +.. |
|*+oEo+. |
|@o o++ |
+----[SHA256]-----+
$ ls -l ~/.ssh/
total 12
-rw------- 1 ansible ansible 1679 sept. 20 09:43 id_rsa
-rw-r--r-- 1 ansible ansible 407 sept. 20 09:43 id_rsa.pub
- Copier la clé publique sur les machines cibles
$ ssh-copy-id -i 192.168.56.102
$ ssh 192.168.56.102
$ ssh-copy-id -i 192.168.56.103
$ ssh 192.168.56.103
$ ssh-copy-id -i 192.168.56.104
$ ssh 192.168.56.104
Fichier d'inventaire minimal
- Créer le fichier d'inventaire
inventories/formation/hosts.
$ mkdir -p inventories/formation
$ cat <<EOF > inventories/formation/hosts
192.168.56.102
192.168.56.103
192.168.56.104
EOF
- Vérifier l'inventaire.
$ ansible all --list-hosts
[WARNING]: provided hosts list is empty,
only localhost is available.
Note that the implicit localhost does not match 'all'
hosts (0):
$ ansible all -i inventories/formation/hosts --list-hosts
hosts (3):
192.168.56.102
192.168.56.103
192.168.56.104
Syntaxe des commandes :
ansible <host-pattern> [options]
- Tester le ping via Ansible.
$ ansible all -i inventories/formation/hosts -m ping
192.168.56.104 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
192.168.56.103 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
192.168.56.102 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
- Ajouter le nom des machines dans l'inventaire
via la syntaxe :
<host-name> ansible_host=<ip-address>
$ cat inventories/formation/hosts
ansible-1 ansible_host=192.168.56.102
ansible-2 ansible_host=192.168.56.103
ansible-3 ansible_host=192.168.56.104
$ ansible all -i inventories/formation/hosts --list-hosts
hosts (3):
ansible-1
ansible-2
ansible-3
- Tester de nouveau le ping et vérifier que les hostnames apparaissent maintenant dans les résultats.
$ ansible all -i inventories/formation/hosts -m ping
ansible-3 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
ansible-2 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
ansible-1 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
- Regrouper les machines en 2 groupes :
centosetdebian.
$ cat inventories/formation/hosts
ansible-1 ansible_host=192.168.56.102
ansible-2 ansible_host=192.168.56.103
ansible-3 ansible_host=192.168.56.104
[centos]
ansible-1
ansible-2
[debian]
ansible-3
- Tester de nouveau le ping mais cette fois-ci uniquement sur les machines CentOS.
$ ansible centos -i inventories/formation/hosts -m ping
ansible-2 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
ansible-1 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
-
Créer un groupe
tousqui regroupera
les groupescentosetdebian. -
Tester de nouveau le ping sur le groupe
tous.
ansible-1 ansible_host=192.168.56.102
ansible-2 ansible_host=192.168.56.103
ansible-3 ansible_host=192.168.56.104
[centos]
ansible-1
ansible-2
[debian]
ansible-3
[tous:children]
centos
debian
-
Créer un snapshot Virtualbox pour les machines
-
ansible-1
-
ansible-2
-
ansible-3
-